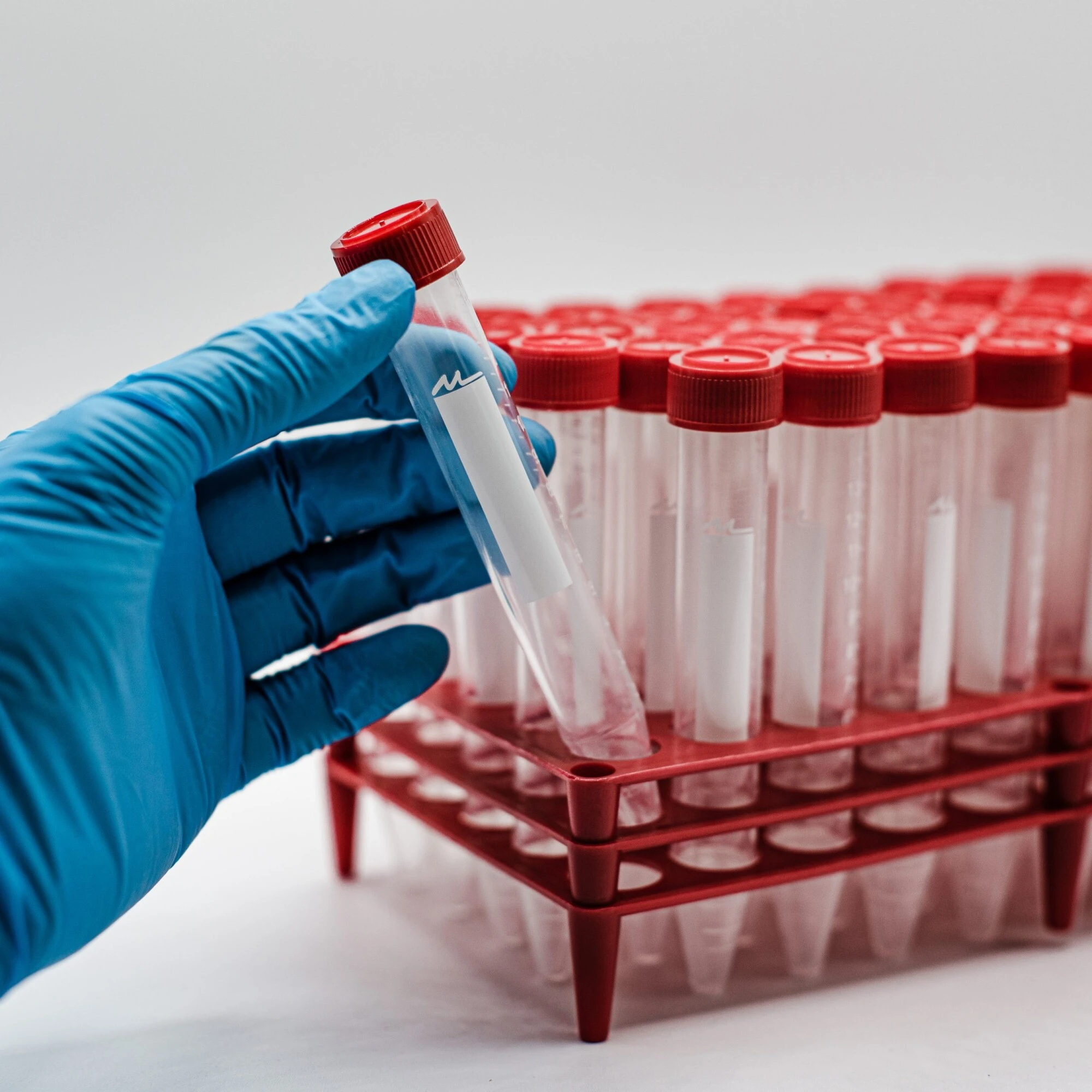
Centrifuge tubes play a vital role in biological laboratories for storing and handling biological samples. They are available in glass and plastic variants, with plastic tubes being preferred for their convenience, durability, and safety features. As a result, plastic centrifuge tubes are widely used in a variety of biological experiments.
Key Features:
Ease of Use:
Centrifuge tubes boast lightweight and portable designs, enabling effortless handling and transportation. Their sealed lid configuration further streamlines sample storage and transfer processes.
Robustness:
Compared to glass alternatives, plastic centrifuge tubes exhibit superior durability and are less susceptible to breakage. This mitigates the potential for sample loss resulting from equipment damage during experimental procedures.
Safety Assurance:
Crafted from non-toxic materials, centrifuge tubes pose minimal risk of sample contamination or harm to laboratory staff. Moreover, their sealed lids effectively prevent sample leakage during centrifugation, enhancing overall experiment safety.
Guidelines for Usage:
Sample Handling and Transfer:
Centrifuge tubes serve as efficient vessels for storing samples before experiments, facilitating subsequent centrifugation and extraction tasks. Moreover, they enable seamless transfer of samples between different stages of experimentation.
Centrifugation Procedure:
During centrifugation, samples are loaded into centrifuge tubes, which are then spun at high speeds in a centrifuge apparatus. These tubes are engineered to endure the centrifugal forces generated during rapid rotation, ensuring the integrity and accuracy of experimental outcomes.
Sample Processing:
Following centrifugation, centrifuge tubes remain indispensable for additional sample processing and extraction steps. For instance, their practical design allows swift separation of supernatant and precipitate, facilitating subsequent analytical procedures and experimentation.
Guidelines for Using Plastic Centrifuge Tubes:
Selection of Suitable Specifications:
Opt for centrifuge tubes with specifications that align with the experimental needs, ensuring they can accommodate the required sample volume and facilitate efficient separation during centrifugation.
Matching Capacities:
Verify that the centrifuge tube's capacity matches the sample volume intended for centrifugation. Oversized capacities risk sample overflow, while undersized capacities may impede proper sample separation.
Consideration of Sample Volume:
When loading samples into centrifuge tubes, ensure the volume is appropriate for the experiment. Excessive sample volumes might lead to excessive foaming during centrifugation, potentially affecting the accuracy of experimental outcomes.
Ensuring Sealing Integrity:
When sealing the lid of the centrifuge tube, verify a secure seal to prevent any sample leakage during centrifugation. Moreover, assess the lid's tightness to avert sample spillage during storage and transfer processes.
Maintenance and Cleaning:
Post-use, promptly clean and maintain centrifuge tubes utilizing designated cleaning solutions and tools to eliminate any lingering samples and contaminants. Regularly inspect and uphold centrifuge tubes to guarantee their continued optimal performance.
In conclusion, plastic centrifuge tubes play a vital role in biological laboratories, offering a plethora of benefits. When employed appropriately, they enhance convenience while elevating experiment accuracy and safety. Hence, it is imperative for laboratory staff to understand the features and proper usage of these tubes, adhering to pertinent guidelines for seamless experimentation.
Next: Effective Pipette Sterilization Techniques
Previous: Pulse Biological News about Pipette Tips

